数据结构之栈和队列实现(TypeScript版)
Comparator实现见前文 前端比较方法的优雅封装最小堆实现见前文 数据结构之 Heap 实现单向链表实现见前文 数据结构之链表实现
1. 队列
1.1 介绍
队列基本操作有两种:入队和出队。从队列的后端位置添加实体,称为入队;从队列的前端位置移除实体,称为出队。
队列中元素先进先出 FIFO(first in, first out)的示意:
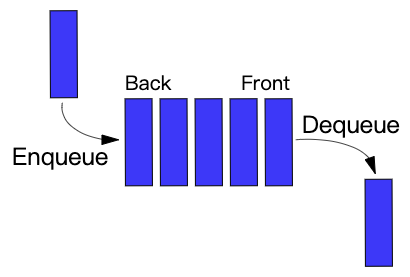
1.2 实现
ts
// queue/Queue.ts
import LinkedList from '../linked-list/LinkedList';
export default class Queue {
public linkedList: LinkedList;
constructor() {
// We're going to implement Queue based on LinkedList since the two
// structures are quite similar. Namely, they both operate mostly on
// the elements at the beginning and the end. Compare enqueue/dequeue
// operations of Queue with append/deleteHead operations of LinkedList.
this.linkedList = new LinkedList();
}
isEmpty() {
return !this.linkedList.head;
}
/**
* Read the element at the front of the queue without removing it.
*/
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return this.linkedList.head.value;
}
/**
* Add a new element to the end of the queue (the tail of the linked list).
* This element will be processed after all elements ahead of it.
*/
enqueue(value: any) {
this.linkedList.append(value);
}
/**
* Remove the element at the front of the queue (the head of the linked list).
* If the queue is empty, return null.
*/
dequeue() {
const removedHead = this.linkedList.deleteHead();
return removedHead ? removedHead.value : null;
}
toString(callback?: (value: any) => any) {
// Return string representation of the queue's linked list.
return this.linkedList.toString(callback);
}
}2. 栈
2.1 介绍
栈这个名称,可类比于一组物体的堆叠(一摞书,一摞盘子之类的)。
栈的元素后进先出(LIFO = last in, first out)操作的示意:
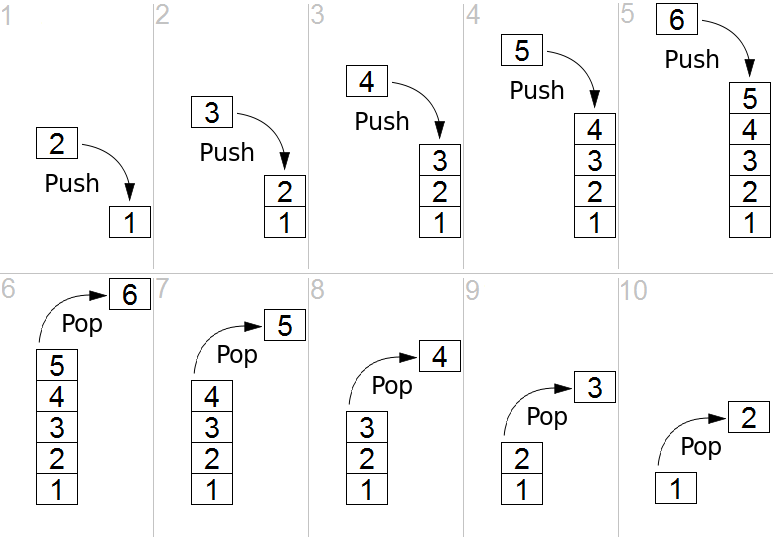
2.2 实现
ts
// stack/Stack.ts
import LinkedList from '../linked-list/LinkedList';
export default class Stack {
public linkedList: LinkedList;
constructor() {
// We're going to implement Stack based on LinkedList since these
// structures are quite similar. Compare push/pop operations of the Stack
// with prepend/deleteHead operations of LinkedList.
this.linkedList = new LinkedList();
}
isEmpty() {
// The stack is empty if its linked list doesn't have a head.
return !this.linkedList.head;
}
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
// If the linked list is empty then there is nothing to peek from.
return null;
}
// Just read the value from the start of linked list without deleting it.
return this.linkedList.head.value;
}
push(value: any) {
// Pushing means to lay the value on top of the stack. Therefore let's just add
// the new value at the start of the linked list.
this.linkedList.prepend(value);
}
pop() {
// Let's try to delete the first node (the head) from the linked list.
// If there is no head (the linked list is empty) just return null.
const removedHead = this.linkedList.deleteHead();
return removedHead ? removedHead.value : null;
}
toArray() {
return this.linkedList.toArray().map(linkedListNode => linkedListNode.value);
}
toString(callback?: (value: any) => any) {
return this.linkedList.toString(callback);
}
}3. 优先队列
3.1 介绍
优先级队列(priority queue) 是一种抽象数据类型,它类似于常规的队列或栈,但每个元素都有与之关联的“优先级”。
在优先队列中,低优先级的元素前面应该是高优先级的元素。 如果两个元素具有相同的优先级,则根据它们在队列中的顺序即可。
优先队列虽通常用堆来实现,但它在概念上与堆不同。 优先队列是一个抽象概念,就像“列表”或“图”这样的抽象概念一样。
正如列表可以用链表或数组实现一样,优先队列可以用堆或各种其他方法实现,例如无序数组。
3.2 实现
ts
// priority-queue/PriorityQueue.ts
import MinHeap from '../heap/MinHeap';
import Comparator, { TypeCompareParam } from '../utils/comparator/Comparator';
// It is the same as min heap except that when comparing two elements
// we take into account its priority instead of the element's value.
export default class PriorityQueue extends MinHeap {
private priorities: Map<any, number>;
constructor() {
// Call MinHeap constructor first.
super();
// Setup priorities map.
this.priorities = new Map();
// Use custom comparator for heap elements that will take element priority
// instead of element value into account.
this.compare = new Comparator(this.comparePriority.bind(this));
}
/**
* Add item to the priority queue.
* @param item - item we're going to add to the queue.
* @param priority - items priority.
*/
add(item: TypeCompareParam, priority = 0) {
this.priorities.set(item, priority);
super.add(item);
return this;
}
/**
* Remove item from priority queue.
* @param item - item we're going to remove.
* @param customFindingComparator - custom function for finding the item to remove
*/
remove(item: TypeCompareParam, customFindingComparator?: Comparator) {
super.remove(item, customFindingComparator);
this.priorities.delete(item);
return this;
}
/**
* Change priority of the item in a queue.
* @param item - item we're going to re-prioritize.
* @param priority - new item's priority.
*/
changePriority(item: TypeCompareParam, priority: number) {
this.remove(item, new Comparator(this.compareValue));
this.add(item, priority);
return this;
}
/**
* Find item by ite value.
*/
findByValue(item: TypeCompareParam) {
return this.find(item, new Comparator(this.compareValue));
}
/**
* Check if item already exists in a queue.
*/
hasValue(item: TypeCompareParam) {
return this.findByValue(item).length > 0;
}
/**
* Compares priorities of two items.
*/
comparePriority(a: TypeCompareParam, b: TypeCompareParam) {
if (this.priorities.get(a) === this.priorities.get(b)) {
return 0;
}
return this.priorities.get(a) < this.priorities.get(b) ? -1 : 1;
}
/**
* Compares values of two items.
*/
compareValue(a: TypeCompareParam, b: TypeCompareParam) {
if (a === b) {
return 0;
}
return a < b ? -1 : 1;
}
}