数据结构之哈希表(散列)实现(TypeScript版)
单向链表实现见前文 数据结构之链表实现
1. 介绍
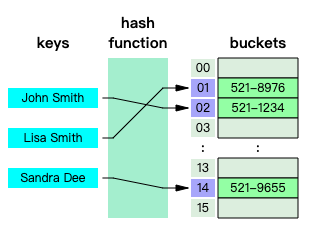
哈希表(hash table 或 hash map) 是一种实现 关联数组(associative array) 的抽象数据类型,该结构可以将 键映射到值 。
哈希表使用 哈希函数/散列函数 来计算一个值在 数组或桶(buckets) 中或 槽(slots) 中对应的索引,可使用该索引找到所需的值。
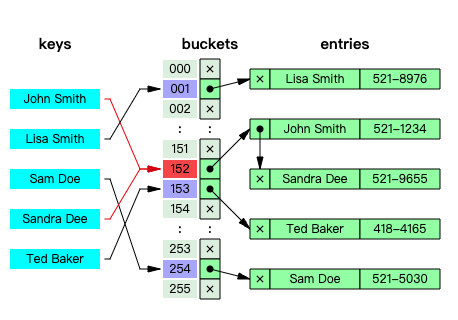
理想情况下,散列函数将为每个键分配给一个唯一的 桶(bucket),但是大多数哈希表设计采用不完美的散列函数,这可能会导致 哈希冲突(hash collisions),也就是散列函数为多个 键(key) 生成了相同的 索引,这种碰撞必须以某种方式进行处理。
通过单独的链接解决哈希冲突:
2. 实现
ts
// hash-table/HashTable.ts
import LinkedList from '../linked-list/LinkedList';
// Hash table size directly affects on the number of collisions.
// The bigger the hash table size the less collisions you'll get.
// For demonstrating purposes hash table size is small to show how collisions
// are being handled.
const defaultHashTableSize = 32;
interface TLinkedNode { key: string; value: any }
export default class HashTable {
public buckets: LinkedList[];
private keys: { string?: string };
constructor(hashTableSize = defaultHashTableSize) {
// Create hash table of certain size and fill each bucket with empty linked list.
this.buckets = Array.from({ length: hashTableSize })
.map(() => new LinkedList());
// Just to keep track of all actual keys in a fast way.
this.keys = {};
}
/**
* Converts key string to hash number.
*/
hash(key: string) {
// For simplicity reasons we will just use character codes sum of all characters of the key
// to calculate the hash.
//
// But you may also use more sophisticated approaches like polynomial string hash to reduce the
// number of collisions:
//
// hash = charCodeAt(0) * PRIME^(n-1) + charCodeAt(1) * PRIME^(n-2) + ... + charCodeAt(n-1)
//
// where charCodeAt(i) is the i-th character code of the key, n is the length of the key and
// PRIME is just any prime number like 31.
const hash = Array.from(key).reduce((hashAccumulator, keySymbol) => hashAccumulator + keySymbol.charCodeAt(0), 0);
// Reduce hash number so it would fit hash table size.
return hash % this.buckets.length;
}
set(key: string, value: any) {
const keyHash = this.hash(key);
this.keys[key] = keyHash;
const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[keyHash];
const node = bucketLinkedList.find({ callback: (nodeValue: TLinkedNode) => nodeValue.key === key });
if (!node) {
// Insert new node.
bucketLinkedList.append({ key, value });
}
else {
// Update value of existing node.
node.value.value = value;
}
}
delete(key: string) {
const keyHash = this.hash(key);
delete this.keys[key];
const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[keyHash];
const node = bucketLinkedList.find({ callback: (nodeValue: TLinkedNode) => nodeValue.key === key });
if (node) {
return bucketLinkedList.delete(node.value);
}
return null;
}
get(key: string) {
const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[this.hash(key)];
const node = bucketLinkedList.find({ callback: (nodeValue: TLinkedNode) => nodeValue.key === key });
return node ? node.value.value : undefined;
}
has(key: string) {
return Object.hasOwnProperty.call(this.keys, key);
}
getKeys() {
return Object.keys(this.keys);
}
/**
* Gets the list of all the stored values in the hash table.
*/
getValues() {
return this.buckets.reduce((values, bucket) => {
const bucketValues = bucket.toArray().map(linkedListNode => linkedListNode.value.value);
return values.concat(bucketValues);
}, []);
}
}